Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs. If left untreated, it can lead to life-threatening complications such as a pulmonary embolism. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and proper management.
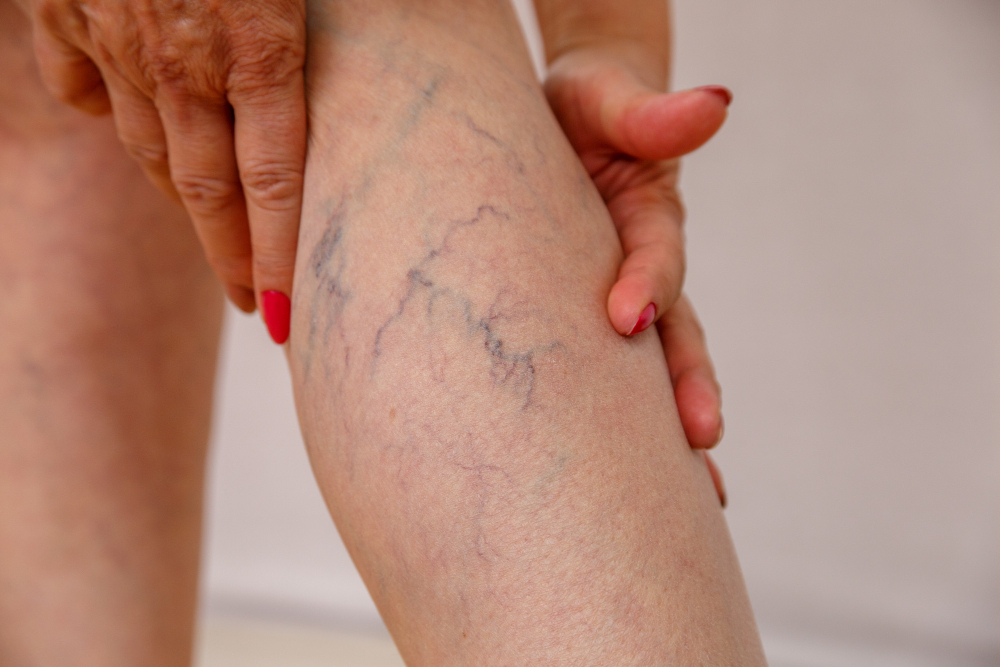
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Several factors can contribute to the development of DVT, including:
- Prolonged immobility: Extended periods of sitting or bed rest, such as during long flights or hospital stays, can reduce blood circulation and increase clotting risk.
- Surgery and physical trauma: Surgical procedures, especially orthopedic or abdominal surgeries, and injuries can damage blood vessels, making clot formation more likely.
- Underlying medical conditions: Chronic illnesses such as cancer, heart disease, and inherited blood clotting disorders may raise the risk of DVT.
- Hormonal influences: Pregnancy, the use of birth control pills, and hormone replacement therapy can increase clotting tendencies, particularly in women.
Symptoms of DVT
Symptoms can vary in intensity and may sometimes be subtle. Common signs include:
- Swelling in one leg, often in the calf or thigh
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area, especially when standing or walking
- Redness or discoloration of the skin
- A feeling of warmth in the swollen or painful area
- Leg cramps, particularly at night
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment Options for DVT
Treatment for DVT focuses on preventing the clot from growing, reducing the risk of complications, and preventing recurrence. Options include:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners): These medications help prevent new clots from forming and stop existing ones from growing.
- Thrombolytic therapy: In more severe cases, clot-dissolving drugs may be administered to break down large clots.
- Compression stockings: These specialized socks apply gentle pressure to the legs, helping to reduce swelling and improve blood flow.
- Surgical procedures: In rare or severe cases, surgical removal of the clot (thrombectomy) may be required.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Who is at risk for DVT?
2. Can DVT be prevented?
3. Is DVT life-threatening?
4. What should I do if I suspect DVT?
5. Can I travel if I have DVT?
Deep Vein Thrombosis may start silently, but its impact can be loud. Staying active, informed, and responsive to symptoms is your best defense. If something feels off — don’t wait. Early care can make all the difference in keeping your life and legs moving forward safely.

Dev Hospitals provides expert care with advanced treatments, ensuring accurate diagnosis and improved patient outcomes.
Contact With Us!
Email: devhospital@gmail.com
Opening Hours: Mon -Sat: 10.00am – 6.00pm